Product Description
ZheJiang Qilu Industrial Co., Ltd has the capacity to guarantee the quality for every step, from raw material (forging), then heating treatment, finally machining. We have our own forging mill, heating teatment shop and machining shop. At present we could supply various of lage main shaft, turbin shaft, cylinder shaft, windy generator shaft, roller shaft, wheel forging, drill bit forging and kinds of irregular parts based on the drawing provided by customers.
Steel material for shaft and forging parts:
| Engineering Steel | |||||
| GB GB/T 700 |
JIS JIS G3101 |
DIN (W-Nr.) EN10571-2 / DIN17100 |
AISI/ASTM ASTM A36 |
BS | OTHERS |
| Q235B | SS400 | S235JR / RST37-2 | A36 | ||
| Q235C | S235J0 / ST37-3 U | ||||
| Q235D | S235J2 | ||||
| GB GB/T1591 |
JIS | DIN (W-Nr.) EN10571-2 / DIN17100 |
AISI/ASTM | BS | OTHERS |
| Q355B | S355JR | ||||
| Q355C | S355J0 / ST52-3U | ||||
| Q355D | S355J2 / ST52-3 N | ||||
| Q355E | S355K2 | ||||
| GB GB/T 699 |
JIS JIS G4051 |
DIN (W-Nr.) EN 10083-2 |
AISI/ASTM ASTM A20 |
BS | OTHERS |
| 1018 | EN2C | ||||
| 20 | S20C | C20 | 1571 | EN3B/070M20 | ASTM A105 |
| 35 | S35C | C30 | 1035 | ||
| 45 | S45C | C45E/1.1191 | 1045 | EN8D/080M40 | |
| 50 | S50C | C50/1.1206 | 1050 | 080M50 | |
| 55 | S55C | C55 | 1055 | EN9/070M55 | |
| GB GB/T 3077 |
JIS JIS G4105/JIS G4103 |
DIN (W-Nr.) EN 15710 |
AISI/ASTM ASTM A29 |
BS BS 970 |
OTHERS |
| 40Cr | SCr440 | 41Cr4(1.7035) | 5140 | ||
| 15CrMo | SCM415 | 16CrMo44/1.7337 | |||
| 20CrMo | SCM420 | 18CrMo4/1.7243 | 4118 | ||
| 30CrMo | SCM430 | 25CrMo4/1.7218 | 4130 | 708A25/708M25 | |
| 42CrMo | SCM440 | 42crmo4/1.7225 | 4140 | EN19/709M40 | |
| SCM445 | 4145 | ||||
| 40CrNiMoA | SNCM 439/SNCM8 | 36CrNiMo4/1.6511 | 4340 | EN24/817M40 | |
| 40NiMoCr10-5/1.6745 | EN26/826M40 | ||||
| 34CrNiMo6 / 1.6582 | 4337 | ||||
| 30CrNiMo16-6/1.6747 | 4330V | EN30B/835M30 | |||
| 32CrMo12/1.7361 | EN40B/722M24 | ||||
| 16CrMnH / 20CrMnTi | 16MnCr5 / 1.7131 | 5115 | |||
| 20CrMn | 20MnCr5 / 1.7147 | ||||
| 15CrNi6/1.5919 | 3115 | ||||
| 16NiCr4/1.5714 | EN351/637M17 | ||||
| 4615/4617 | EN34/665M17 | ||||
| 14NiCr14/1.5752 | 3310/3415 | EN36/655M13 | |||
| 15NiCrMo16-5/1.6723 | EN39/835M15 | ||||
| 17CrNiMo6 | 18CrNiMo7-6 (1.6587) | 4815 | |||
| 20CrNiMo | SNCM220 | 1.6523/21NiCrMo2 | 8620 | 805M20 | |
| 20CrNiMo5 | EN353 | ||||
| GCr15 | SUJ2 | 52100/1.3505 | EN31/535A99 | ||
| 38CrMoAl | SACM645 | 41CrAlMo7/34CrAlMo5 | 905M39/905M31 | 41CrAlMo74(ISO) | |
ZheJiang Qilu Industrial Co., Ltd were already engaged in exporting steel for 11 years, could supply a great variety of hot forged, hot rolled and cold drawn Steels , including engineering steel, cold work tool steel, hot work tool steel, plastic mold steel, spring steel, high speed steel, stainless steel etc., besides Qilu Industrial also has their own heating treatment shop and machining shop to provide heating treatment, cutting and further machining service.
Since 2008 year, ZheJiang Qilu Industrial has the right to export all FORGED STEEL behalf of Qilu Speical Steel Co.,ltd which is specialized in smelting and forging of special steel since 1965 year, now Qilu special steel is 1 of the biggest manufacturer of forged product in China.The forged products are used in Automotive, Aerospace, Power Generation, Oil & Gas, Transportation and Industrial.
Till 2013 year, many customers need HOT ROLLED and COLD DRAWN steel from Qilu Industrial, in order to provide one-stop solution to our customers, Qilu Industrial began to cooperate with Xihu (West Lake) Dis.bei Special Steel (HangZhou and HangZhou mill), Baosteel, Tiangong International, Changcheng Special Steel for hot rolled tool steel, cooperate with HangZhou Speical Steel, HangZhou HangZhou Speical Steel, Shagang Group, CZPT Group for hot rolled engineering steel. Now we already set up the warehouse in HangZhou and HangZhou City, more than 20000 tons ex-stock could be supplied with kinds of sizes.
Then from 2018 year, Qilu Industrial decide to provide further manufacturer processing service, at present we could supply various of lage main shaft, turbin shaft, cylinder shaft, windy generator shaft, roller shaft, wheel forging, drill bit forging and kinds of irregular parts based on the drawing provided by customers.
Qilu Industrial is the professional one-stop steel manufacturer, stockist and exporter in China, our customers spread all over the world, include West Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Middle Asia, Africa, Australia, etc.
The company owns advanced special steel smelting facilities and forging processing equipments, the main steel-making equipment include 2 sets of 50t ultra-high power electric arc furnaces,2 sets of 60t LF refining furnaces,1 set of 60t vacuum degassing refining CZPT and 4 sets of 1-20t electroslag re-melting furnaces.
The main forging equipments mainly include:3 sets of 5t electro-hydraulic hammers, 1 set of high-speed forging units of 800t,1600t,2000t and 4500t respectively.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Central Spindle |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT6-IT9 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Stepped Shaft |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
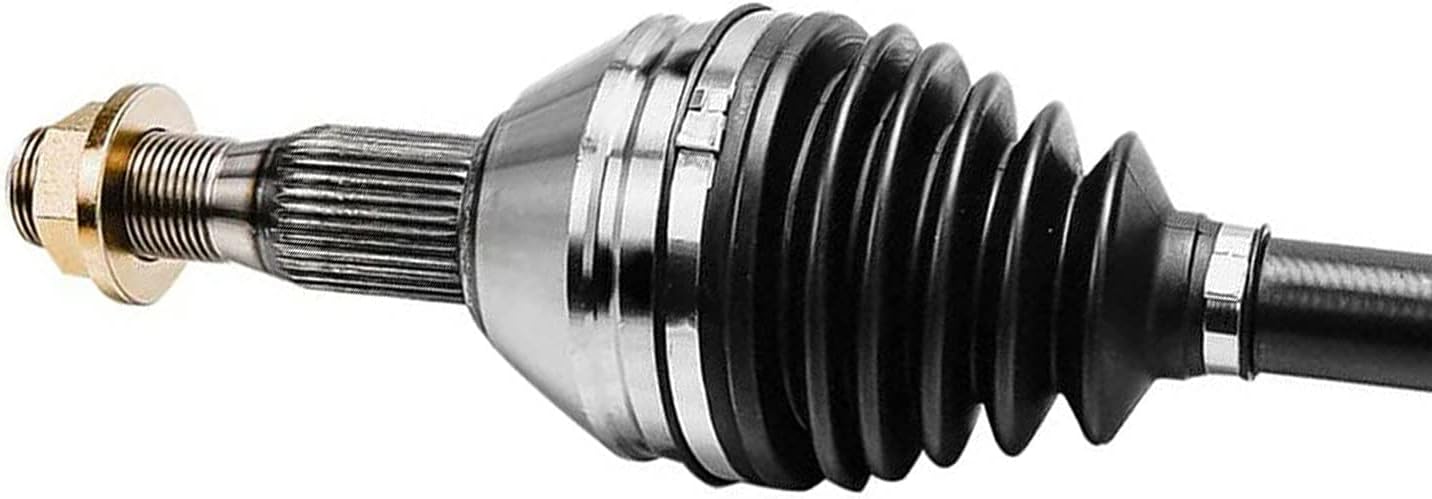

Where can I buy axle seals for preventing fluid leaks in my vehicle’s axles?
When it comes to purchasing axle seals to prevent fluid leaks in your vehicle’s axles, there are several options available. Here are some places where you can buy axle seals:
1. Automotive Parts Stores:
Visit local automotive parts stores such as AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts, O’Reilly Auto Parts, or NAPA Auto Parts. These stores typically have a wide range of automotive seals, including axle seals, in stock. You can either visit the physical store or check their online catalogs to find the specific axle seal you need for your vehicle.
2. Dealerships:
If you prefer to purchase genuine OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) axle seals, consider visiting a dealership authorized by your vehicle’s manufacturer. Dealerships often carry original parts that are specifically designed for your vehicle make and model. Contact your local dealership’s parts department to inquire about the availability of axle seals for your vehicle.
3. Online Retailers:
Online retailers like Amazon, eBay, and RockAuto offer a wide range of automotive parts, including axle seals. These platforms provide the convenience of browsing and purchasing axle seals from the comfort of your home. Make sure to check the product details, specifications, and customer reviews before making a purchase.
4. Local Mechanics and Repair Shops:
Local mechanics and repair shops often have access to a variety of automotive seals, including axle seals. They can source and install the appropriate seals for your vehicle during maintenance or repair services. Reach out to trusted local mechanics or repair shops in your area and inquire about their availability and pricing for axle seals.
5. Manufacturer’s Online Stores:
Some vehicle manufacturers have their own online stores where you can purchase genuine OEM parts, including axle seals. Visit the official website of your vehicle’s manufacturer and look for their online parts store. You can search for the specific axle seal needed for your vehicle using your vehicle identification number (VIN) or the model details.
6. Salvage Yards:
If you are looking for cost-effective options or rare axle seals, salvage yards can be an option. Salvage yards specialize in selling used parts salvaged from vehicles. However, when purchasing from salvage yards, it’s important to carefully inspect the condition and compatibility of the axle seals to ensure they are suitable for your vehicle.
When purchasing axle seals, make sure to provide accurate information about your vehicle’s make, model, and year to ensure you get the correct seals that fit your vehicle’s axle specifications. Additionally, consider factors such as the quality of the seals, warranty options, and return policies when making your purchase decision.
Remember, if you are unsure about the specific axle seals required for your vehicle or need assistance with installation, it is recommended to consult with a qualified mechanic or technician who can guide you in selecting the right seals and ensure proper installation to prevent fluid leaks in your vehicle’s axles.

Can you provide insights into the advancements in axle technology in recent years?
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in axle technology to enhance performance, efficiency, and safety in vehicles. Here are some insights into the key advancements:
- Lightweight Materials:
- Electronic Differential:
- Advanced Axle Bearings:
- Electric Axles:
- Active Suspension Integration:
- Improved Sealing and Lubrication:
- Autonomous Vehicle Integration:
One notable advancement is the use of lightweight materials in axle construction. Manufacturers have increasingly utilized materials such as aluminum alloys and high-strength steels to reduce the weight of axles without compromising strength and durability. Lighter axles contribute to improved fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
Electronic differentials, also known as eDiffs, have gained popularity in recent years. They utilize sensors, actuators, and control algorithms to monitor and distribute torque between the wheels more efficiently. Electronic differentials enhance traction, stability, and handling by actively managing torque distribution, especially in vehicles equipped with advanced stability control systems.
Axle bearings have seen advancements in design and materials to reduce friction, improve efficiency, and enhance durability. For example, the use of roller bearings or tapered roller bearings has become more prevalent, offering reduced frictional losses and improved load-carrying capacity. Some manufacturers have also introduced sealed or maintenance-free bearings to minimize maintenance requirements.
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, electric axles have emerged as a significant technological advancement. Electric axles integrate electric motors, power electronics, and gear systems into the axle assembly. They eliminate the need for traditional drivetrain components, simplify vehicle packaging, and offer benefits such as instant torque, regenerative braking, and improved energy efficiency.
Advancements in axle technology have facilitated the integration of active suspension systems into axle designs. Active suspension systems use sensors, actuators, and control algorithms to adjust the suspension characteristics in real-time, providing improved ride comfort, handling, and stability. Axles with integrated active suspension components offer more precise control over vehicle dynamics.
Axles have seen advancements in sealing and lubrication technologies to enhance durability and minimize maintenance requirements. Improved sealing systems help prevent contamination and retain lubricants, reducing the risk of premature wear or damage. Enhanced lubrication systems with better heat dissipation and reduced frictional losses contribute to improved efficiency and longevity.
The development of autonomous vehicles has spurred advancements in axle technology. Axles are being designed to accommodate the integration of sensors, actuators, and communication systems necessary for autonomous driving. These advancements enable seamless integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving features, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
It’s important to note that the specific advancements in axle technology can vary across different vehicle manufacturers and models. Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts continue to drive further innovations in axle design, materials, and functionalities.
For the most up-to-date and detailed information on axle technology advancements, it is advisable to consult automotive manufacturers, industry publications, and reputable sources specializing in automotive technology.
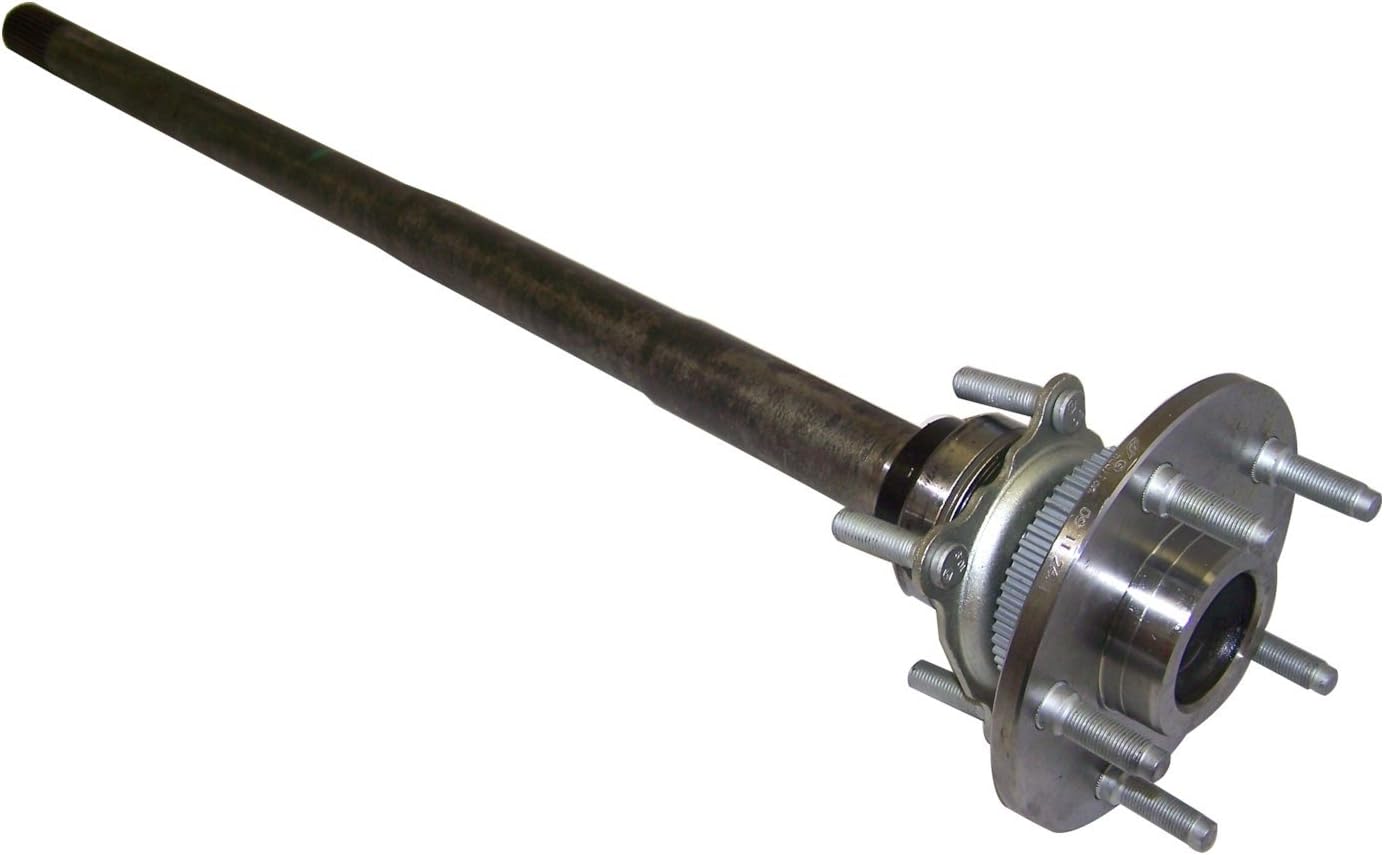

How do solid axles differ from independent axles in terms of performance?
When comparing solid axles and independent axles in terms of performance, there are several key differences to consider. Both types of axles have their advantages and disadvantages, and their suitability depends on the specific application and desired performance characteristics. Here’s a comparison of solid axles and independent axles:
| Aspect | Solid Axles | Independent Axles |
|---|---|---|
| Load-Bearing Capability | Solid axles have high load-bearing capability due to their robust and sturdy construction. They can handle heavy loads and provide excellent stability, making them suitable for off-road vehicles, heavy-duty trucks, and towing applications. | Independent axles typically have lower load-bearing capability compared to solid axles. They are designed for lighter loads and offer improved ride comfort and handling characteristics. They are commonly used in passenger cars, sports cars, and vehicles with a focus on maneuverability and road performance. |
| Wheel Articulation | Solid axles have limited wheel articulation due to their connected and rigid design. This can result in reduced traction and compromised wheel contact with the ground on uneven terrain. However, solid axles provide excellent traction in situations where the weight distribution on all wheels needs to be maintained, such as in off-road or rock-crawling applications. | Independent axles offer greater wheel articulation as each wheel can move independently of the others. This allows the wheels to better conform to uneven terrain, maximizing traction and maintaining contact with the ground. Independent axles provide improved off-road capability, enhanced handling, and better ride comfort. |
| Ride Comfort | Due to their rigid design, solid axles generally provide a stiffer and less compliant ride compared to independent axles. They transmit more road shocks and vibrations to the vehicle’s occupants, resulting in a rougher ride quality. | Independent axles are known for providing better ride comfort. Each wheel can react independently to road imperfections, absorbing shocks and vibrations more effectively. This leads to a smoother and more comfortable ride, particularly on paved roads and surfaces with minor irregularities. |
| Handling and Stability | Solid axles offer excellent stability due to their connected nature. They provide better resistance to lateral forces, making them suitable for high-speed stability and towing applications. However, the rigid axle design can limit overall handling and maneuverability, particularly in tight corners or during quick direction changes. | Independent axles generally offer improved handling and maneuverability. Each wheel can react independently to steering inputs, allowing for better cornering performance and agility. Independent axles are commonly found in vehicles where precise handling and responsive steering are desired, such as sports cars and performance-oriented vehicles. |
| Maintenance and Repair | Solid axles are relatively simpler in design and have fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain and repair. They are often more resistant to damage and require less frequent servicing. However, if a component within the axle assembly fails, the entire axle may need to be replaced. | Independent axles are typically more complex in design and have multiple moving parts, such as control arms, CV joints, or bearings. This complexity can result in higher maintenance and repair costs. However, if a failure occurs, only the affected component needs to be replaced, reducing repair expenses compared to replacing the entire axle. |
It’s important to note that advancements in suspension and axle technologies have resulted in various hybrid systems that combine features of solid and independent axles. These systems aim to provide a balance between load-bearing capability, wheel articulation, ride comfort, and handling performance based on specific application requirements.
In summary, solid axles excel in load-bearing capability, stability, and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications and off-road conditions. Independent axles offer improved ride comfort, better wheel articulation, enhanced handling, and maneuverability, making them suitable for passenger cars and vehicles focused on road performance. The choice between solid axles and independent axles depends on the specific needs and priorities of the vehicle or machinery.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China Good quality Forged Steel Shaft Head/Roll Shaft /Drive Shaft
Product Description
| Steel Grade | 4140,4130,A1050,F11,5140,304L,316L,321,P11,F22,4340 |
| 1.2344, 17CrNiMo6, 20MnMo, S355NL | |
| 18CrNiMo7-6 | |
| 42CrMo, 40CrNiMo |
| Processing Object: | Metal |
|---|---|
| Molding Style: | Forging |
| Molding Technics: | Gravity Casting |
| Application: | Agricultural Machinery Parts |
| Material: | Steel |
| Heat Treatment: | Tempering |
| Samples: |
US$ 10000/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
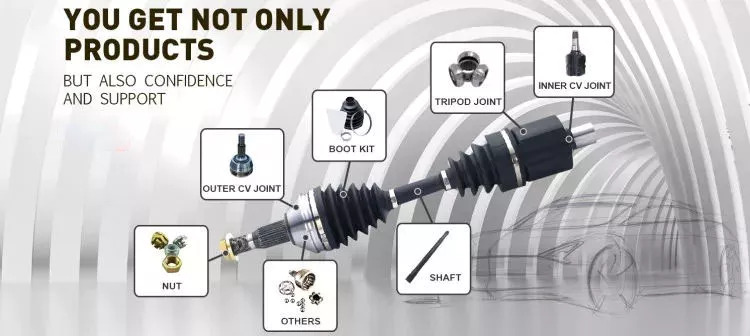
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

What is a drive shaft and how does it function in vehicles and machinery?
A drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a mechanical component that plays a critical role in transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels or other driven components in vehicles and machinery. It is commonly used in various types of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and agricultural or industrial machinery. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a drive shaft is and how it functions:
1. Definition and Construction: A drive shaft is a cylindrical metal tube that connects the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of one or more tubular sections with universal joints (U-joints) at each end. These U-joints allow for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components.
2. Power Transmission: The primary function of a drive shaft is to transmit rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. In vehicles, the drive shaft connects the transmission or gearbox output shaft to the differential, which then transfers power to the wheels. In machinery, the drive shaft transfers power from the engine or motor to various driven components such as pumps, generators, or other mechanical systems.
3. Torque and Speed: The drive shaft is responsible for transmitting both torque and rotational speed. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine or power source, while rotational speed is the number of revolutions per minute (RPM). The drive shaft must be capable of transmitting the required torque without excessive twisting or bending and maintaining the desired rotational speed for efficient operation of the driven components.
4. Flexible Coupling: The U-joints on the drive shaft provide a flexible coupling that allows for angular movement and compensation of misalignment between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components. As the suspension system of a vehicle moves or the machinery operates on uneven terrain, the drive shaft can adjust its length and angle to accommodate these movements, ensuring smooth power transmission and preventing damage to the drivetrain components.
5. Length and Balance: The length of the drive shaft is determined by the distance between the engine or power source and the driven wheels or components. It should be appropriately sized to ensure proper power transmission and avoid excessive vibrations or bending. Additionally, the drive shaft is carefully balanced to minimize vibrations and rotational imbalances, which can cause discomfort, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature wear of drivetrain components.
6. Safety Considerations: Drive shafts in vehicles and machinery require proper safety measures. In vehicles, drive shafts are often enclosed within a protective tube or housing to prevent contact with moving parts and reduce the risk of injury in the event of a malfunction or failure. Additionally, safety shields or guards are commonly installed around exposed drive shafts in machinery to protect operators from potential hazards associated with rotating components.
7. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, or excessive play in the U-joints, inspecting the drive shaft for any cracks or deformations, and lubricating the U-joints as recommended by the manufacturer. Proper maintenance helps prevent failures, ensures optimal performance, and prolongs the service life of the drive shaft.
In summary, a drive shaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotational power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components in vehicles and machinery. It functions by providing a rigid connection between the engine/transmission and the driven wheels or components, while also allowing for angular movement and compensation of misalignment through the use of U-joints. The drive shaft plays a crucial role in power transmission, torque and speed delivery, flexible coupling, length and balance considerations, safety, and maintenance requirements. Its proper functioning is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and machinery.


editor by CX 2023-09-13