Product Description
HOB 63×100 HOB -63-150 HOB -63×250 hydraulics cylinders , air hydraulic cylinder
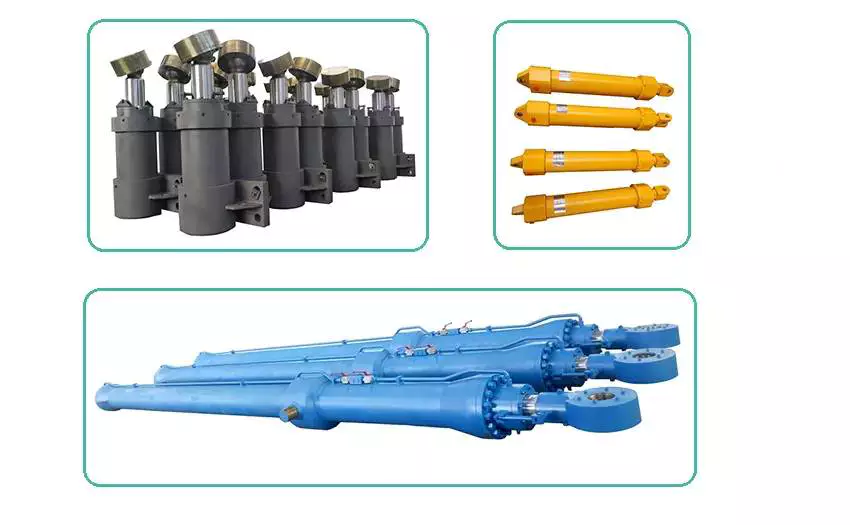
HOB series hydro-cylinder is heavy type hydraulic cylinder, give the derive cylinder of double rod type and stroke adjustable type, varies of installments are optional to meet different requirement, also can be customized. Widely used in hydro-power engineering projects, metallurgical industry, construction industry, aviation and cosmonautical industry, cranes, textile & chemical industry, plastic injection mounding machines, elevators, ship-lifts, offshore well-drilling platforms, etc.
Model:
| HOB 40×50 | HOB 50×50 | HOB 63×50 | HOB 80×50 | HOB 100×50 | HOB 125×50 |
| HOB 40×100 | HOB 50×100 | HOB 63×100 | HOB 80×100 | HOB 100×100 | HOB 125×100 |
| HOB 40×150 | HOB 50×150 | HOB 63×150 | HOB 80×150 | HOB 100×150 | HOB 125×150 |
| HOB 40×200 | HOB 50×200 | HOB 63×200 | HOB 80×200 | HOB 100×200 | HOB 125×200 |
| HOB 40×250 | HOB 50×250 | HOB 63×250 | HOB 80×250 | HOB 100×250 | HOB 125×250 |
| HOB 40×300 | HOB 50×300 | HOB 63×300 | HOB 80×300 | HOB 100×300 | HOB 125×300 |
| HOB 40×350 | HOB 50×350 | HOB 63×350 | HOB 80×350 | HOB 100×350 | HOB 125×350 |
| HOB 40×400 | HOB 50×400 | HOB 63×400 | HOB 80×400 | HOB 100×400 | HOB 125×400 |
| HOB 40×450 | HOB 50×450 | HOB 63×450 | HOB 80×450 | HOB 100×450 | HOB 125×450 |
| HOB 40×500 | HOB 50×500 | HOB 63×500 | HOB 80×500 | HOB 100×500 | HOB 125×500 |
| HOB 40×600 | HOB 50×600 | HOB 63×600 | HOB 80×600 | HOB 100×600 | HOB 125×600 |
| HOB 40×700 | HOB 50×700 | HOB 63×700 | HOB 80×700 | HOB 100×700 | HOB 125×700 |
| HOB 40×800 | HOB 50×800 | HOB 63×800 | HOB 80×800 | HOB 100×800 | HOB 125×800 |
| HOB 40×900 | HOB 50×900 | HOB 63×900 | HOB 80×900 | HOB 100×900 | HOB 125×900 |
| HOB 40×1000 | HOB 50×1000 | HOB 63×1000 | HOB 80×1000 | HOB 100×1000 | HOB 125×1000 |
| HOB 150×50 | HOB 160×50 | HOB180x50 | HOB 200×50 | HOB 250×50 |
| HOB 150×100 | HOB 160×100 | HOB 180×100 | HOB 200×100 | HOB 250×100 |
| HOB 150×150 | HOB 160×150 | HOB 180×150 | HOB 200×150 | HOB 250×150 |
| HOB 150×200 | HOB 160×200 | HOB180x200 | HOB200x200 | HOB 250×200 |
| HOB 150×250 | HOB 160×250 | HOB 180×250 | HOB 200×250 | HOB 250×250 |
| HOB 150×300 | HOB 160×300 | HOB 180×300 | HOB 200×300 | HOB 250×300 |
| HOB 150×350 | HOB 160×350 | HOB 180×350 | HOB 200×350 | HOB 250×350 |
| HOB150x400 | HOB 160×400 | HOB180x400 | HOB 200×400 | HOB 250×400 |
| HOB 150×450 | HOB 160×450 | HOB 180×450 | HOB 200×450 | HOB 250×450 |
| HOB 150×500 | HOB 160×500 | HOB 180×500 | HOB 200×500 | HOB 250×500 |
| HOB 150×600 | HOB 160×600 | HOB 180×600 | HOB 200×600 | HOB 250×600 |
| HOB 150×700 | HOB 160×700 | HOB 180×700 | HOB 200×700 | HOB 250×700 |
| HOB 150×800 | HOB 160×800 | HOB 180×800 | HOB 200×800 | HOB 250×800 |
| HOB 150×900 | HOB 160×900 | HOB 180×900 | HOB 200×900 | HOB 250×900 |
| HOB 150×1000 | HOB 160×1000 | HOB 180×1000 | HOB 200×1000 | HOB 250×1000 |
Product details:
| Certification: | GS, CE, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Pressure: | Medium Pressure |
| Work Temperature: | High Temperature |
| Acting Way: | Double Acting |
| Working Method: | Straight Trip |
| Adjusted Form: | Regulated Type |
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do hydraulic cylinders compare to other methods of force generation like electric motors?
Hydraulic cylinders and electric motors are two different methods of force generation with distinct characteristics and applications. While both hydraulic cylinders and electric motors can generate force, they differ in terms of their working principles, performance attributes, and suitability for specific applications. Here’s a detailed comparison of hydraulic cylinders and electric motors:
1. Working Principle:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders generate force through the conversion of fluid pressure into linear motion. They consist of a cylinder barrel, piston, piston rod, and hydraulic fluid. When pressurized hydraulic fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the piston, causing the piston rod to extend or retract, thereby generating linear force.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors generate force through the conversion of electrical energy into rotational motion. They consist of a stator, rotor, and electromagnetic field. When an electrical current is applied to the motor’s windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor, causing it to rotate and generate torque.
2. Force and Power:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are known for their high force capabilities. They can generate substantial linear forces, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that require lifting, pushing, or pulling large loads. Hydraulic systems can provide high force output even at low speeds, allowing for precise control over force application. However, hydraulic systems typically operate at lower speeds compared to electric motors.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors excel in providing high rotational speeds and are commonly used for applications that require rapid motion. While electric motors can generate significant torque, they tend to have lower force output compared to hydraulic cylinders. Electric motors are suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.
3. Control and Precision:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems offer excellent control over force, speed, and positioning. By regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid, the force and speed of hydraulic cylinders can be precisely controlled. Hydraulic systems can provide gradual acceleration and deceleration, allowing for smooth and precise movements. This level of control makes hydraulic cylinders well-suited for applications that require precise positioning, such as in industrial automation or construction equipment.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors also offer precise control over speed and positioning. Through motor control techniques such as varying voltage, frequency, or pulse width modulation (PWM), the rotational speed and position of electric motors can be accurately controlled. Electric motors are commonly used in applications that require precise speed control, such as robotics, CNC machines, or servo systems.
4. Efficiency and Energy Consumption:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems can be highly efficient, especially when properly sized and designed. However, hydraulic systems typically have higher energy losses due to factors such as fluid leakage, friction, and heat generation. The overall efficiency of a hydraulic system depends on the design, component selection, and maintenance practices. Hydraulic systems require a hydraulic power unit to pressurize the hydraulic fluid, which consumes additional energy.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors can have high efficiency, especially when operated at their optimal operating conditions. Electric motors have lower energy losses compared to hydraulic systems, primarily due to the absence of fluid leakage and lower friction losses. The overall efficiency of an electric motor depends on factors such as motor design, load conditions, and control techniques. Electric motors require an electrical power source, and their energy consumption depends on the motor’s power rating and the duration of operation.
5. Environmental Considerations:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic systems typically use hydraulic fluids that can pose environmental concerns if they leak or are not properly disposed of. The choice of hydraulic fluid can impact factors such as biodegradability, toxicity, and potential environmental hazards. Proper maintenance and leak prevention practices are essential to minimize the environmental impact of hydraulic systems.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors are generally considered more environmentally friendly since they do not require hydraulic fluids. However, the environmental impact of electric motors depends on the source of electricity used to power them. When powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, electric motors can offer a greener solution compared to hydraulic systems.
6. Application Suitability:
– Hydraulic Cylinders: Hydraulic cylinders are commonly used in applications that require high force output, precise control, and durability. They are widely employed in industries such as construction, manufacturing, mining, and aerospace. Hydraulic systems are well-suited for heavy-duty applications, such as lifting heavy objects, operating heavy machinery, or controlling large-scale movements.
– Electric Motors: Electric motors are widely used in various industries and applications that require rotational motion, speed control, and precise positioning. They are commonly found in appliances, transportation, robotics, HVAC systems, and automation. Electric motorsare suitable for applications that involve continuous rotary motion, such as driving conveyor belts, rotating machinery, or powering vehicles.In summary, hydraulic cylinders and electric motors have different working principles, force capabilities, control characteristics, efficiency levels, and application suitability. Hydraulic cylinders excel in providing high force output, precise control, and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Electric motors, on the other hand, offer high rotational speeds, precise speed control, and are commonly used for applications that involve continuous rotary motion. The choice between hydraulic cylinders and electric motors depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of motion, force output, control precision, and environmental considerations.
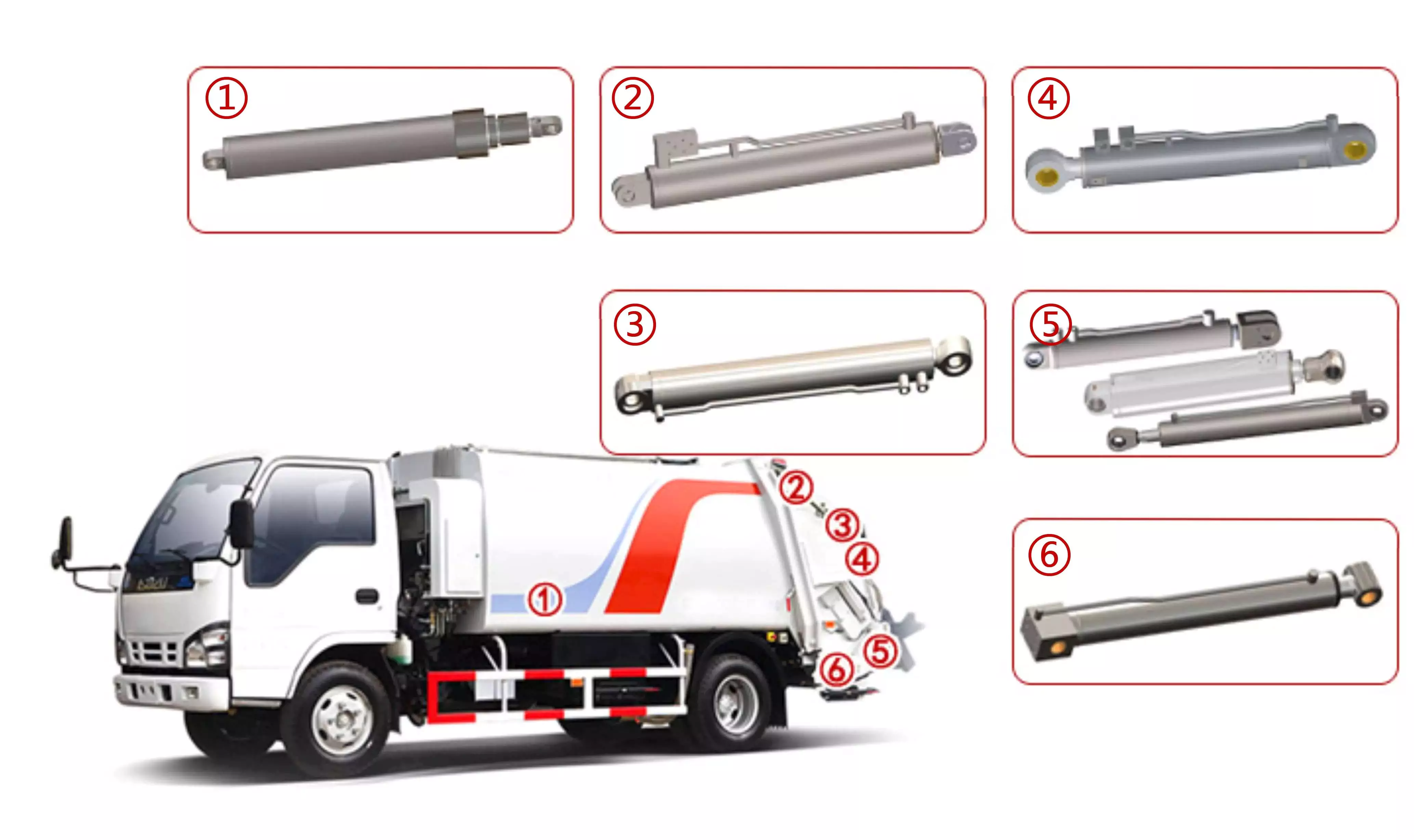

How do hydraulic cylinders contribute to the efficiency of agricultural tasks like plowing?
Hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in improving the efficiency of agricultural tasks, including plowing. These cylinders provide several benefits that enhance the performance and productivity of agricultural machinery. Let’s explore how hydraulic cylinders contribute to the efficiency of plowing and other agricultural tasks:
- Powerful Force Generation: Hydraulic cylinders are capable of generating high forces, which is essential for tasks like plowing. The hydraulic system supplies pressurized fluid to the cylinders, converting hydraulic energy into mechanical force. This force is then utilized to drive plow blades through the soil, overcoming resistance and facilitating efficient soil penetration. The power generated by hydraulic cylinders ensures effective plowing, even in tough or compacted soil conditions.
- Adjustable Working Depth: Hydraulic cylinders allow for easy and precise adjustment of the plow’s working depth. By controlling the extension or retraction of the hydraulic cylinder, farmers can adjust the depth of the plow blades according to soil conditions, crop requirements, or their specific preferences. This adjustability enhances efficiency by ensuring optimal soil tillage and minimizing unnecessary energy expenditure. Farmers can adapt the plowing depth to different field areas, optimizing the use of resources and promoting uniform crop growth.
- Responsive Control: Hydraulic systems offer highly responsive control, enabling farmers to make quick adjustments during plowing operations. Hydraulic cylinders respond rapidly to changes in hydraulic pressure and valve settings, allowing for immediate modifications in the plow’s position, depth, or angle. This responsiveness enhances efficiency by facilitating on-the-go adjustments based on soil variations, obstacles, or changing field conditions. Farmers can maintain precise control over the plow’s performance, ensuring effective soil tillage and minimizing the risk of crop damage.
- Implement Versatility: Hydraulic cylinders enable the attachment of various implements to agricultural machinery, expanding their functionality and versatility. In the context of plowing, hydraulic cylinders allow for the attachment and detachment of plow blades or other tillage implements. This versatility enables farmers to adapt their equipment to different soil types, field sizes, or specific plowing requirements. By using hydraulic cylinders, farmers can easily switch between different implements, optimizing their equipment for specific tasks and maximizing efficiency.
- Efficient Time Management: Hydraulic cylinders contribute to time efficiency in agricultural tasks like plowing. With hydraulic systems, farmers can operate plows at higher speeds while maintaining control and precision. The responsive nature of hydraulic cylinders allows for efficient turning, maneuvering, and repositioning of plows, minimizing downtime and optimizing field coverage. This time efficiency translates into increased productivity and reduced overall operational costs. Farmers can accomplish plowing tasks more quickly, allowing them to cover larger field areas in less time.
In summary, hydraulic cylinders significantly contribute to the efficiency of agricultural tasks like plowing. Through powerful force generation, adjustable working depth, responsive control, implement versatility, and efficient time management, hydraulic systems equipped with cylinders enhance the performance and productivity of agricultural machinery. These contributions allow farmers to accomplish plowing tasks more effectively, optimize field operations, and achieve improved overall efficiency in their agricultural practices.

How do hydraulic cylinders handle variations in load and pressure during operation?
Hydraulic cylinders are designed to handle variations in load and pressure during operation, making them versatile and efficient in various applications. Hydraulic systems use the principle of transmitting force through incompressible fluid to generate linear motion. Here’s a detailed explanation of how hydraulic cylinders handle variations in load and pressure:
1. Load Handling:
– Hydraulic cylinders are capable of handling different loads by utilizing the principle of Pascal’s law. According to Pascal’s law, when pressure is applied to a fluid in a confined space, the pressure is transmitted equally in all directions. In a hydraulic cylinder, the force applied to the piston results in an equal force output at the rod end of the cylinder. The size of the piston and the pressure exerted determine the force generated by the cylinder. Therefore, hydraulic cylinders can handle a wide range of loads by adjusting the pressure applied to the fluid.
2. Pressure Compensation:
– Hydraulic systems incorporate pressure compensation mechanisms to handle variations in pressure during operation. Pressure compensating valves or regulators are often used to maintain a consistent pressure in the hydraulic system, regardless of load changes. These valves automatically adjust the flow rate or pressure to ensure stable and controlled operation of the hydraulic cylinder. By compensating for pressure variations, hydraulic cylinders can maintain a consistent force output and prevent damage or instability due to excessive pressure.
3. Control Valves:
– Control valves play a crucial role in managing variations in pressure and load during hydraulic cylinder operation. Directional control valves, such as spool valves or poppet valves, control the flow of hydraulic fluid into and out of the cylinder, enabling precise control of the cylinder’s extension and retraction. By adjusting the position of the control valve, the speed and force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder can be regulated to match the load and pressure requirements of the application. Control valves allow for efficient handling of variations in load and pressure by providing fine-tuned control over the hydraulic system.
4. Accumulators:
– Hydraulic accumulators are often used to handle fluctuations in pressure and load. Accumulators store hydraulic fluid under pressure, which can be released or absorbed as needed to compensate for sudden changes in load or pressure. When the load on the hydraulic cylinder decreases, the accumulator releases stored fluid to maintain pressure and prevent pressure spikes. Conversely, when the load on the cylinder increases, the accumulator absorbs excess fluid to maintain system stability. By utilizing accumulators, hydraulic cylinders can effectively handle variations in load and pressure, ensuring smooth and controlled operation.
5. Feedback and Control Systems:
– Advanced hydraulic systems may incorporate feedback and control systems to monitor and adjust the operation of hydraulic cylinders in real-time. Position sensors or pressure sensors provide feedback on the cylinder’s position, force, and pressure, allowing the control system to make continuous adjustments to optimize performance. These systems can automatically adapt to variations in load and pressure, ensuring precise control and efficient operation of the hydraulic cylinder.
6. Design Considerations:
– Proper design considerations, such as selecting the appropriate cylinder size, piston diameter, and rod diameter, are essential for handling variations in load and pressure. The design should account for the maximum anticipated load and pressure conditions to ensure the hydraulic cylinder operates within its specified range. Additionally, the selection of suitable seals, materials, and components that can withstand the anticipated load and pressure variations is crucial for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the hydraulic cylinder.
By utilizing the principles of hydraulic systems, incorporating pressure compensation mechanisms, employing control valves and accumulators, and implementing feedback and control systems, hydraulic cylinders can effectively handle variations in load and pressure during operation. These features and design considerations allow hydraulic cylinders to adapt and perform optimally in a wide range of applications and operating conditions.

editor by CX 2023-09-13